The Precession Cycle is Approximately ______years, Duration, Effects & More
Introdction to The Precession Cycle is Approximately ______years
The precession cycle is a fascinating phenomenon that has significant effects on our planet over a span of approximately 26,000 years. It refers to the gradual wobble of Earth’s axis, a process driven primarily by the gravitational pull exerted by the Sun and the Moon. This slow, cyclical motion impacts various aspects of our planet, including its climate and the stars visible from Earth.
During the precession cycle, Earth’s rotational axis slowly shifts, causing changes in the way we experience time and seasons. Over thousands of years, this wobble alters the orientation of the Earth’s axis, which, in turn, influences the climate and weather patterns on a long-term scale. For example, the precession cycle plays a role in the shifts of the Earth’s position relative to the stars, which is why certain constellations appear in the sky at different times or even at different positions as the centuries pass.
In addition to its effect on the climate, the precession cycle also influences the Earth’s axial tilt, which has long-term consequences for the planet’s seasons. By understanding precession, scientists can better predict how climate patterns might evolve over millennia. It provides insight into ancient astronomical observations and how early civilizations might have interpreted the changing patterns of the stars.
While this natural process is too slow to notice in our lifetimes, it’s essential for understanding the broader dynamics of Earth’s relationship with the cosmos. The study of precession allows us to grasp the subtle, yet profound, changes that occur over extended periods of time and to appreciate the intricate balance between gravitational forces, climate, and the universe’s vast expanses.
In summary, the precession cycle is a powerful example of the long-term forces shaping our world. It affects not only the visibility of stars but also plays a crucial role in understanding Earth’s climate changes over the course of thousands of years. This knowledge helps us anticipate how our planet may evolve, both astronomically and environmentally, far beyond the span of human history.
What is the Precession Cycle?
The precession cycle refers back to the gradual, sluggish wobble of Earth’s axis, pushed more often than not by using the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon. This diffused shift influences Earth’s tilt and performs a significant role in diverse lengthy-term changes, inclusive of altering seasonal patterns, the placement of the North Pole, and the timing of equinoxes and solstices. One of the more intriguing effects of this cycle is the movement of stars; the celebrities we see these days received’t continue to be inside the identical positions inside the sky inside the distant future.
Spanning about 26,000 years, the precession cycle represents a gradual, continuous trade in Earth’s orientation relative to the stars and different celestial our bodies. This massive cycle is a part of broader herbal methods that affect Earth’s weather and astronomical capabilities over millennia.
Duration of the Precession Cycle
The full precession cycle lasts about 26,000 years, a period so prolonged that its effects aren’t sizeable on human timescales. Since human lifespans are plenty shorter than this cycle, its have an effect on on Earth’s climate and big name visibility takes location over millennia. However, over this time frame, the shift in Earth’s axis can drastically modify various factors, inclusive of famous person patterns and seasonal adjustments.
Understanding the Precession Cycle
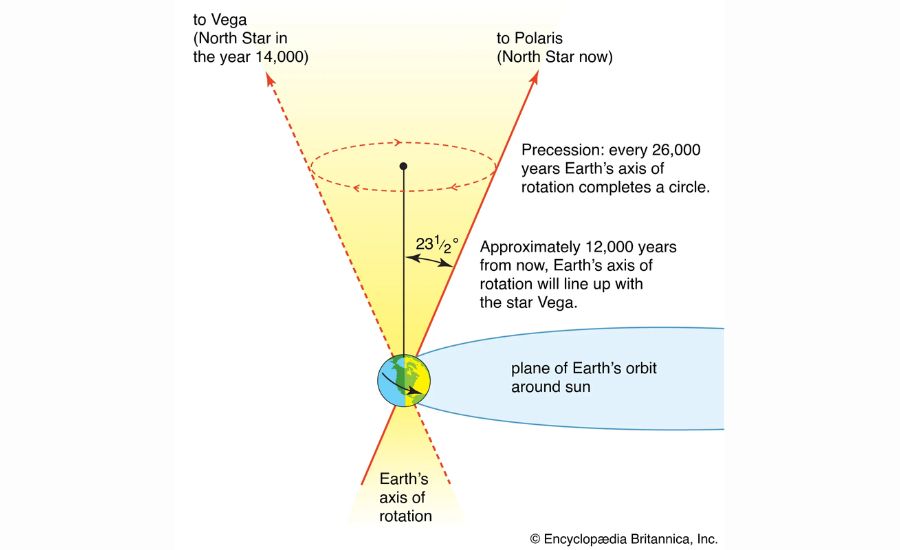
Earth’s axis is tilted at an attitude of about 23.Five degrees relative to the aircraft of its orbit, known as the plane of the ecliptic. Over time, gravitational forces from the Sun and Moon exert strain on Earth’s equatorial bulge, causing the planet’s axis to hint a round route in area. This movement forms a cone-lengthy-hooked up sample that spans 26,000 years to finish.
As this sluggish wobble keeps, the placement of the North Pole gradually shifts. This change is so diffused that it takes lots of years for the celebrities visible inside the night sky to shift in significant approaches. For example, the modern North Star, Polaris, will no longer serve as the pole famous person after approximately 12,000 years. In its place, Vega, a bright megastar inside the Lyra constellation, will sooner or later take over this position, highlighting the long-time period nature of this celestial cycle.
Ultimately, the precession cycle is a fascinating aspect of Earth’s movement, demonstrating how cosmic forces can shape the very stars we observe and influence climate patterns over long periods. While its effects are imperceptible in the short term, this cycle plays a crucial role in Earth’s astronomical and environmental evolution across millennia.
The Effects of the Precession Cycle on Earth’s Climate and Astronomy:
The precession cycle, even though a sluggish and subtle manner, has profound impacts on Earth’s climate and the visibility of stars, in particular whilst discovered over long timescales. These results, spanning thousands of years, provide insight into the complex courting among Earth’s movements and its environment.
Seasonal Changes:
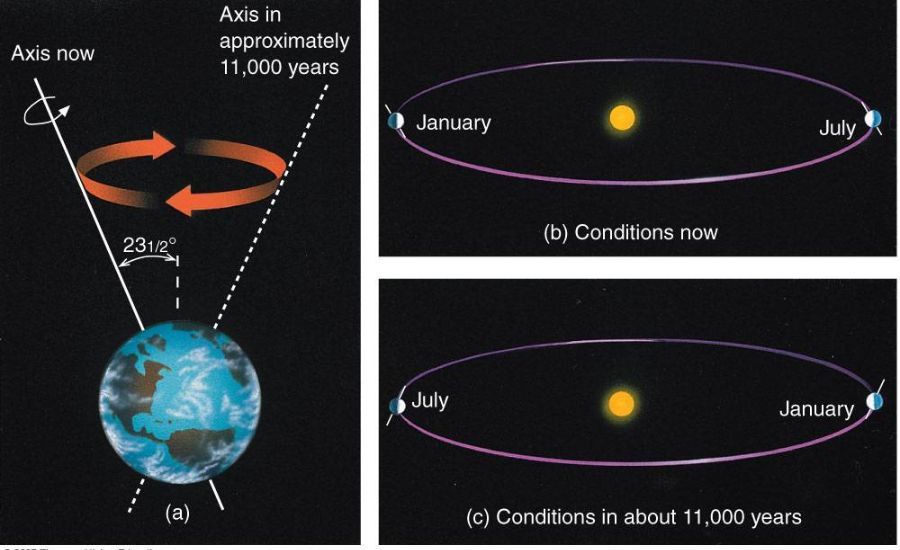
One of the important thing effects of the precession cycle is its have an impact on on the timing of the seasons. As Earth’s axis progressively wobbles, its tilt relative to its orbit around the Sun shifts. Over the route of 26,000 years, this results in a sluggish change within the timing of equinoxes and solstices. For example, at the same time as the Northern Hemisphere currently reviews its wintry weather solstice in December, thousands of years from now, this occasion will arise during a distinct time of year. The axial shift reasons those seasonal markers to arise at extraordinary points in Earth’s orbit, slowly converting the rhythm of the calendar.
Changes in Star Visibility:
The precession cycle also influences the celebrities we see within the night sky. As Earth’s axis wobbles, the positions of the stars relative to our planet slowly trade. This consequences in shifts in which constellations are seen during particular times of the 12 months. For example, Polaris, presently known as the North Star, will now not keep this function after around 12,000 years because of the sluggish shift of Earth’s rotational axis. Vega, a star within the Lyra constellation, will update it as the new North Star, despite the fact that this variation will take millennia to spread.
Effects on Earth’s Climate (Milankovitch Cycles):
The precession cycle is an crucial trouble of the Milankovitch cycles, which consist of versions in Earth’s axial tilt, orbit, and precession. These cycles are perception to be liable for long-term climate adjustments, together with the onset of ice a long time. Precession, combined with shifts in Earth’s tilt and its orbit, influences the amount of sun radiation reaching Earth at distinct latitudes in some unspecified time in the future of the 12 months.
Over lots of years, these changes affect the intensity and timing of seasons, that could impact the increase and retreat of ice sheets—a key thing in global climate patterns. While precession is an vital part of these weather shifts, it works at the side of the other Milankovitch cycles to create the alternating heat and cold intervals related to Earth’s ice a long time. Together, those cycles force huge modifications in Earth’s climate over vast durations of time.
Understanding the precession cycle and its impact on the planet helps us better comprehend the gradual yet profound changes occurring in both our climate and the starry sky. These long-term shifts highlight the dynamic and interconnected nature of Earth’s movements within the broader cosmos.
FAQs
1. What is the precession cycle?
The precession cycle is a gradual wobble in Earth’s axis, caused by the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon. This slow, continuous movement alters Earth’s orientation over a period of approximately 26,000 years. The cycle affects the timing of seasons, the position of stars, and Earth’s climate patterns.
2. How long does the precession cycle last?
The precession cycle lasts about 26,000 years. This incredibly long period means its effects aren’t noticeable in our lifetimes, but over thousands of years, it causes significant shifts in things like star positions and seasonal timing.
3. Why does Earth’s axis wobble?
Earth’s axis wobbles due to the gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon on Earth’s equatorial bulge. This pressure causes Earth’s axis to trace a circular path in space, completing a full cycle over 26,000 years.
4. How does the precession cycle affect the seasons?
As Earth’s axis shifts during the precession cycle, the timing of equinoxes and solstices gradually changes. For example, in thousands of years, the Northern Hemisphere’s winter solstice, which currently occurs in December, will take place during a different time of year.
5. How does precession affect star visibility?
The precession cycle causes the positions of stars in the night sky to change over long periods. For instance, the current North Star, Polaris, will no longer be the pole star in about 12,000 years. Instead, the star Vega will take its place.
6. What is the connection between precession and Earth’s climate?
Precession is part of a larger system known as the Milankovitch cycles, which influence Earth’s long-term climate patterns. These cycles, which include changes in Earth’s tilt, orbit, and precession, affect how much solar radiation Earth receives, impacting the planet’s climate over thousands of years. This, in turn, influences the timing of ice ages and warm periods.
7. How does the precession cycle impact Earth’s axial tilt?
As part of the precession cycle, Earth’s axial tilt gradually shifts, which affects the intensity and timing of seasons. This long-term shift in tilt can have lasting effects on Earth’s climate and the growth and retreat of ice sheets.
8. Can we observe the effects of precession in our lifetime?
While the precession cycle takes place over thousands of years, its effects are too gradual to notice within a single human lifetime. However, by studying these long-term changes, scientists can predict how Earth’s climate and the night sky will evolve over many millennia.
9. What happens to the North Star during the precession cycle?
The North Star, currently Polaris, will no longer hold this position in about 12,000 years due to the precession of Earth’s axis. Vega, a bright star in the Lyra constellation, will eventually take over as the new North Star.
10. Why is the precession cycle important to study?
The precession cycle helps scientists understand Earth’s movements and how they affect both our climate and the stars. Studying precession gives us insight into the long-term dynamics of Earth’s environment and helps us predict how the planet will evolve astronomically and climatically in the distant future.
Final Words
In end, the precession cycle is a notable and gradual procedure that influences Earth’s orientation, weather, and the stars we study. Spanning approximately 26,000 years, this cycle is too sluggish to word in our lifetimes however performs a critical role in shaping lengthy-time period adjustments. It impacts the timing of seasons, shifts in famous person visibility, and contributes to great climate versions through the Milankovitch cycles. By know-how precession, we advantage insights into the dynamic courting among Earth, the cosmos, and our environment, helping us appreciate the widespread and subtle modifications that spread over millennia.
For more Information About Information visit idealrular


![[Img]Https://Lookpic.Com/Cdn/I2/S/05282024182719-002.Jpg[/Img], Breeze & More 7 [Img]Https://Lookpic.Com/Cdn/I2/S/05282024182719-002.Jpg[/Img], Breeze & More](https://idealrular.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Maury_Ange-Faith-Martinez-Daquan-And-Jorge-61-768x469.jpg)

